Creating a User for Krill through the /admin Panel
Access the admin panel:
To do this, we need to go to https://XXX.phicus.es/admin using the credentials we usually use for Krill.
Once inside, we will see this panel:
We go to Users, where we can see all the users we have created:
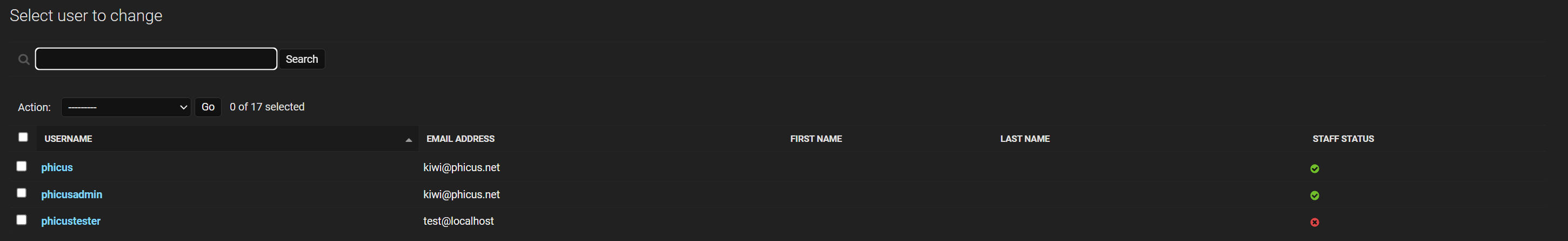
At the top right, we can add a new user using "Add User":
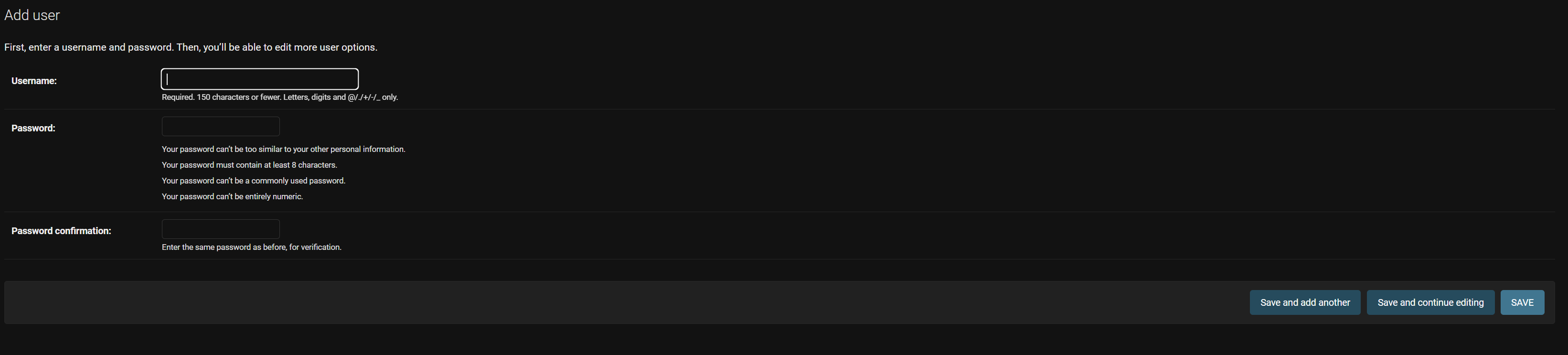
This screen appears, where we must enter the Username and the password twice.
Once we have created the user, we can manage the permissions:
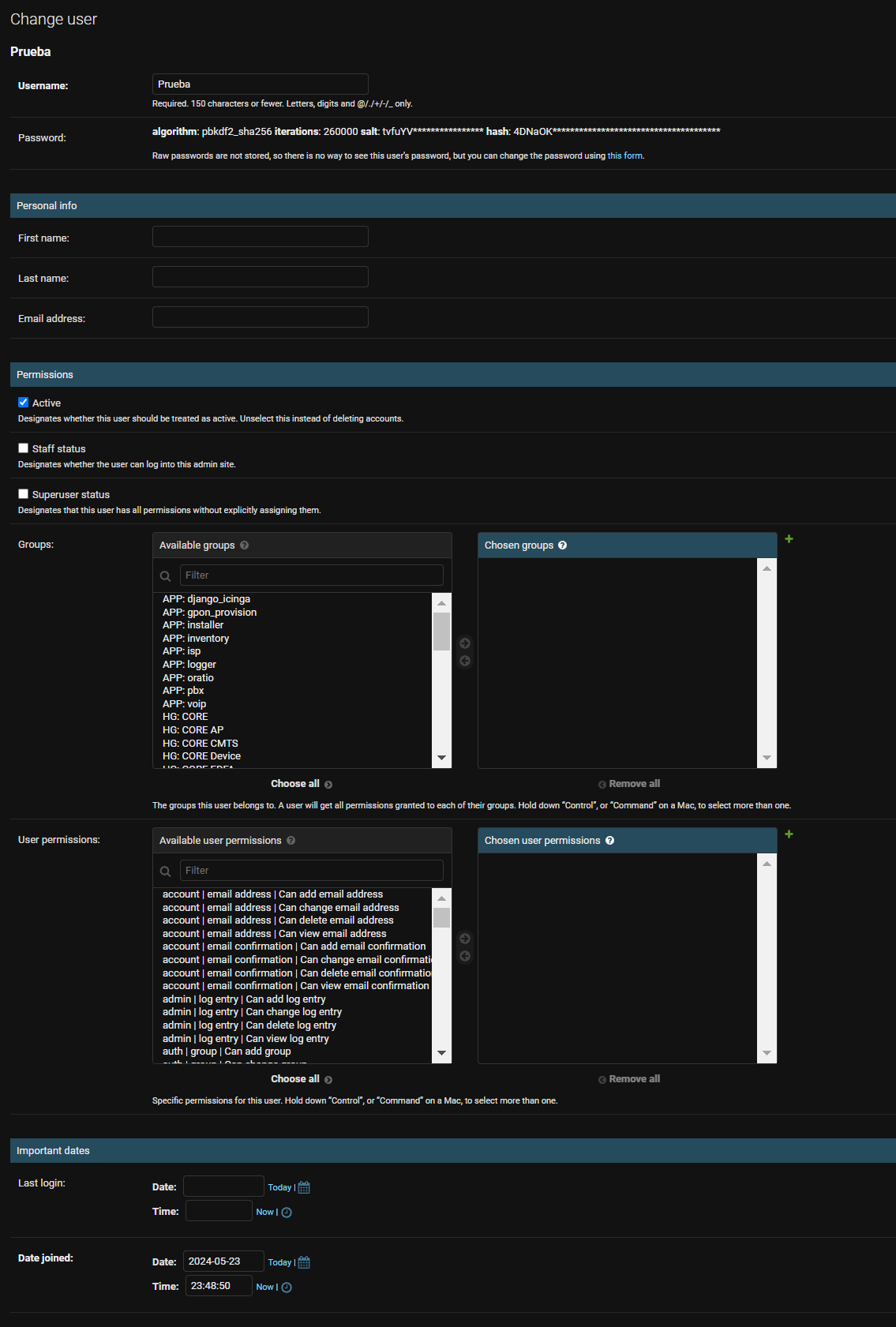
After this, we must grant permissions to the corresponding realm, as the network can be divided into realms, and each of these has different visibility.
Let’s assume that the realm to be modified is the main and default one, called "cpe":
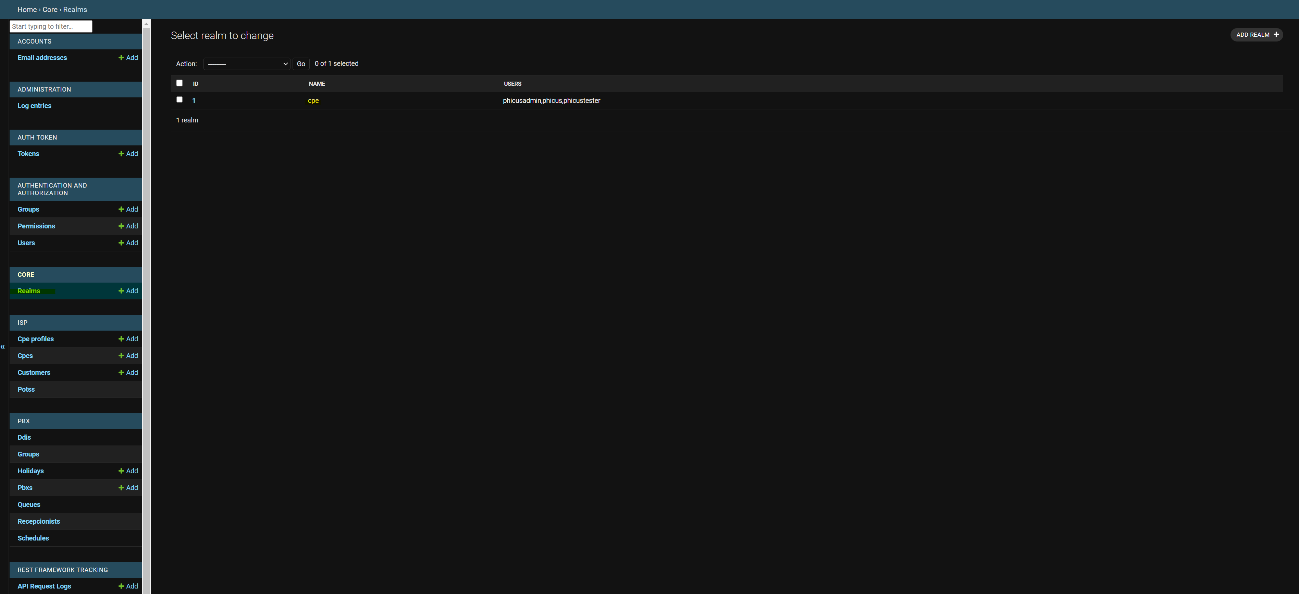
Once we see this image, we need to enter the realm itself, in this case by clicking on "1", to manage the different users who have access to the realm:
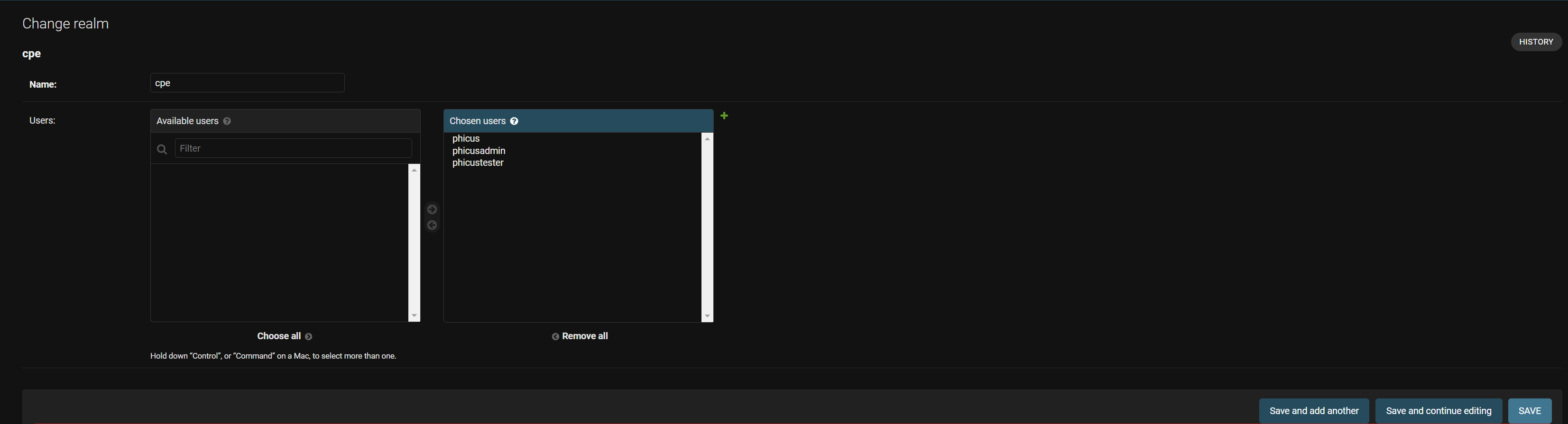
Here, we can insert the different users who have permission to view the CPE Realm. The process would be exactly the same for any realm.
Explanation of Groups and Permissions in the Administration Panel
Groups
APP
Applications are specific modules within your system that offer different functionalities. Each application handles a particular part of the system.
Example
- APP inventory: Manages everything related to inventory, such as products, stock, and goods in/out.
- APP voip: Manages VoIP (Voice over IP) services, handling calls and voice communications over the Internet.
HG (Host Groups)
Host groups are collections of devices or services managed together. These groups allow organizing and monitoring different components of the infrastructure.
Example
- HG CORE Servers: Includes all the main servers of the system, essential for the network and services to function.
- HG CORE Router: Groups all central routers, crucial for data traffic management.
Realm
Realms are specific domains within the system that group similar devices or services, facilitating their management and monitoring.
Example
- realm:cpeethernet: Refers to the domain of CPE (Customer Premises Equipment) devices using Ethernet technology.
- realm:swtdocsis: Includes devices in the SWT Realm that use DOCSIS technology for data transmission over coaxial cable.
Permissions
Permission Structure
Each permission is presented in the format 'application | model | action'.
- Application: The part of the system where the permission is applied (e.g., account, admin).
- Model: The type of data or entity to which the permission applies (e.g., email address, user).
- Action: The operation that is allowed, such as add (add), change (change), delete (delete), or view (view).
Permission Examples
- account | email address | Can add email address: Allows the user to add a new email address in the account application.
- auth | user | Can change user: Allows the user to modify other users' data in the authentication application.
- icingadb | hostgroup | Can monitor CORE Servers: Allows the user to monitor the main servers in the CORE host group.
- isp | Customer | Can view Customer: Allows the user to view customer data in the ISP (Internet Service Provider) application.
Functioning
Assigning Permissions
Each user in your system can be assigned various permissions. These permissions determine what actions they can perform within the specific system applications.
- Example: A user with the 'Can view email address' permission can view email addresses but cannot modify or delete them.
User Groups
Users can be grouped into 'Groups' that have a common set of permissions. This facilitates permission management for multiple users who need the same accesses. Instead of assigning permissions individually to each user, they are assigned to a group, and users are added to this group.
Example
- Support Group: Could have permissions such as 'Can view Customer' and 'Can view isp'. All users in the Support Group will inherit these permissions.
- Administrators Group: Would have broader permissions, such as 'Can add user', 'Can delete user', 'Can view all data', allowing full system management.
